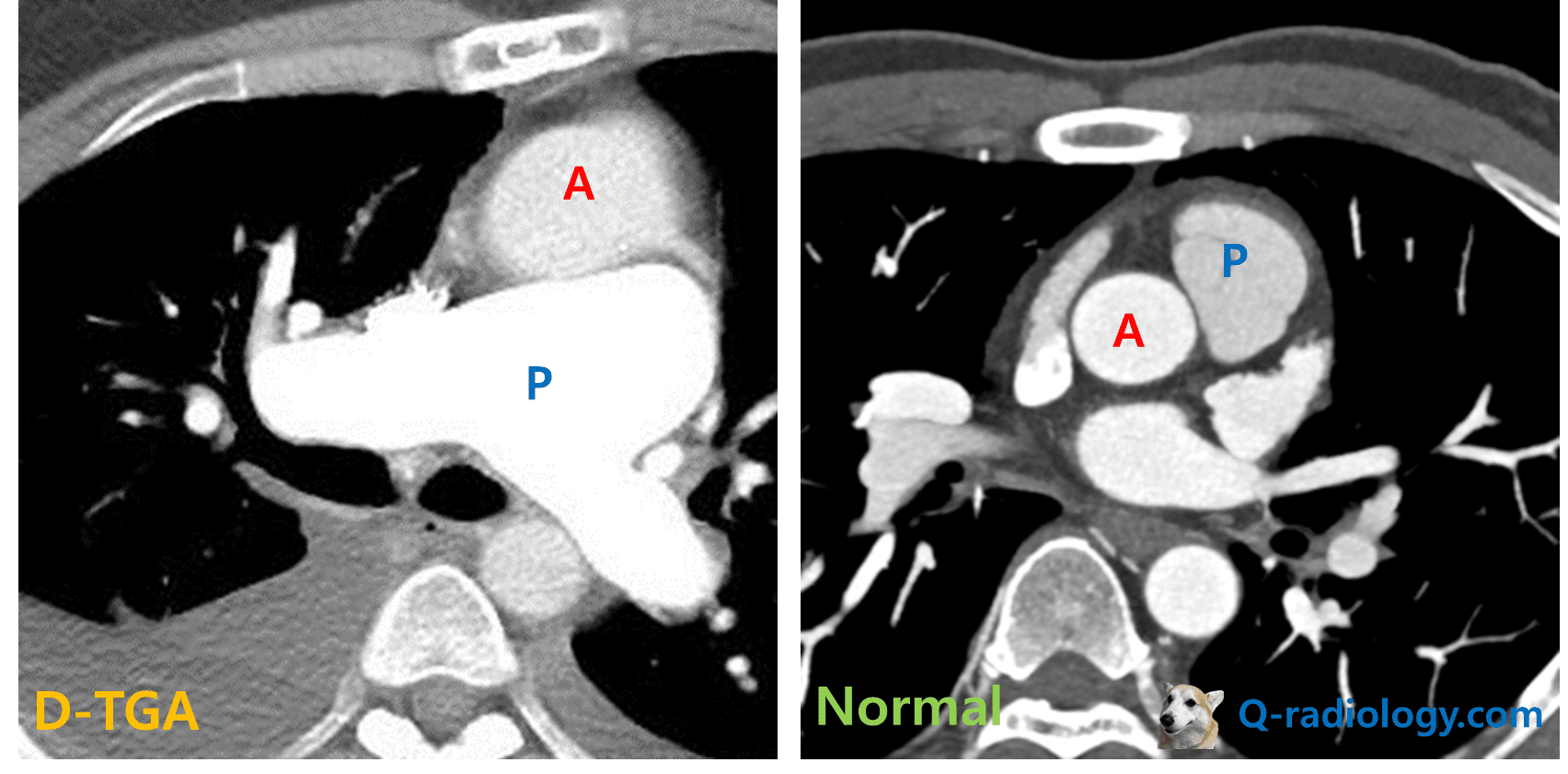
Aortic stenosis (Acquired and congenital)
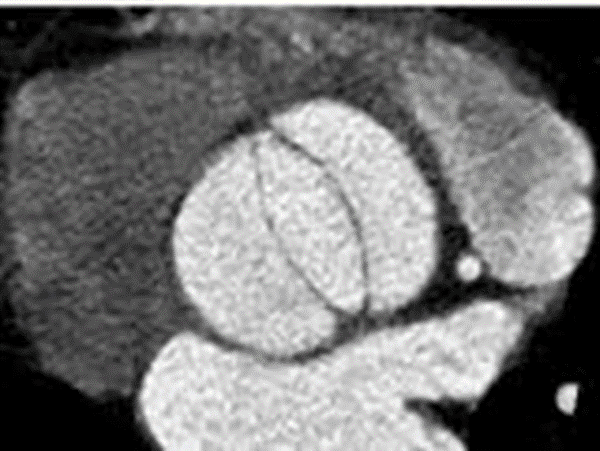
Normal aortic valve : 3-4cm2< 2cm2 : clinically significant aortic stenosis< 0.8cm2 : severe aortic stenosis Aortic stenosis is the most common form of valvular heart disease for valve replacement. Transcatheter arotic valve implantation or replacement (TAVI/TAVR) Reference)Charles S. White, Linda B. Haramati, Joseph Jen-Sho Chen, and Jeffrey M. Levsky (2014), Cardiac Imaging, Oxford university pressMarc … Read more