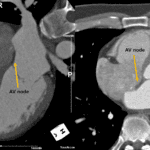
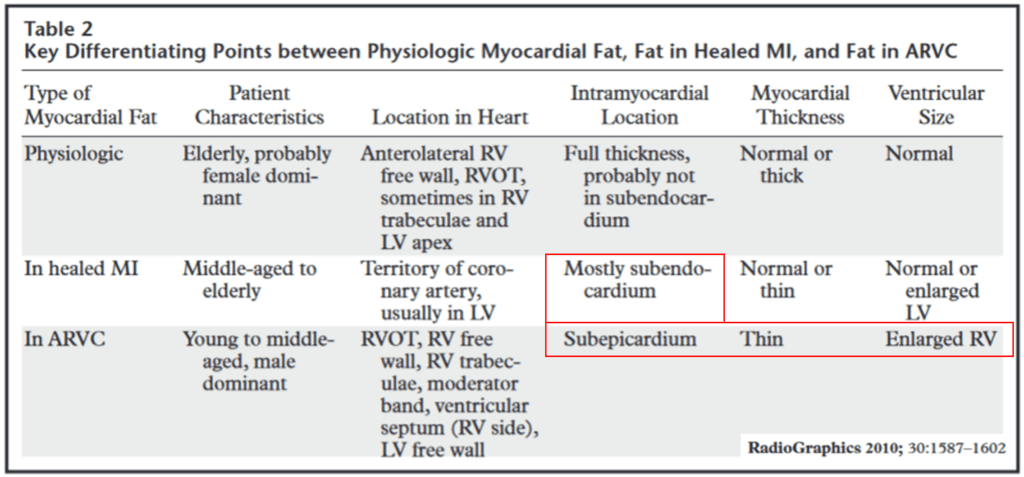
Fat deposition of the right ventricle
Right ventricular fat infiltration is not rare in asymptomatic elderly patient.
RV fat infiltration occurs in about 17 % of asymptomatic subjects on CT.
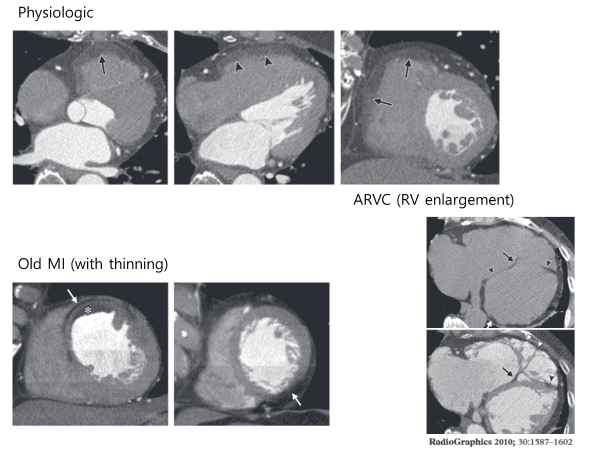
Fat infiltrations were most frequently seen in the superior wall of the base, middle segments, and the right ventricular outlow tract with normal or increased thickness
Myocardial Fat Scarring
CT imaging usually reveals that the prevalence of myocardial fat scarring at LV is 22–62 % among patients with a history of MI.
Myocardial fat scarring caused by healed MI is of thin and linear or curvilinear configuration along the vascular territory of culprit coronary artery.
CT imaging studies usually shows subendocardial fat scarring of normal thickness or thin.
Middle or subepicardial layer of myocardial fat scarring has rarely been observed
Fibrofatty replacement of right ventricular myocardium in Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD) should be excluded when right ventricular fat infiltration is found in a symptomatic, young patient.
The RV free wall of ARVD is usually almost thin because of fibrofatty replacement extending from the epicardium toward the endocardium.
In contrast, with physiologic fat, the RV free wall maintains normal thickness or is sometimes thickened
Follow my instagram

See other posting about cardiovascular imaging