Inflammatory myopathy is a group of disorders that are characterized by muscle inflammation and weakness. The most common types of inflammatory myopathy are polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and inclusion body myositis.
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are autoimmune disorders, which means that they are caused by the immune system attacking healthy cells in the body. Inclusion body myositis is not fully understood, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of autoimmune and degenerative processes.
Imaging
- Location
- DM, PM bilaterally symmetric
- Early: Proximal lower extremities; usually vasti
- Progresses to upper extremity, neck, and pharyngeal muscles
- IBM, FM: Focal involvement
- DM, PM bilaterally symmetric
- Radiographic findings
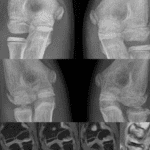
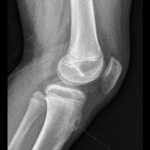
- Soft tissue calcification (20-50% of DM)
- Classic description is sheet-like
- Many cases are globular or amorphous
- Osteopenia, related to steroid therapy
- Associated insufficiency fracture, especially in spine
- Osteonecrosis, related to steroid therapy
- Intramedullary infarct: Patchy or serpiginous
- Subchondral infarct: Relative sclerosis, surrounding osteopenia, followed by subchondral fracture line
- Soft tissue calcification (20-50% of DM)
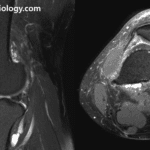
- MR findings
- Subcutaneous edema
- Fasciitis
- Inflammatory myositis
- calcification low signal on all sequences
- Increased signal intensity on fluid-sensitive sequences ; STIR highly sensitive
- individual muscle edema ranges from patchy to diffuse

See other posting about MSK imaging