Myocardial disease : Ischemia and infarction
- 1. Stunned and Hibernating myocardium
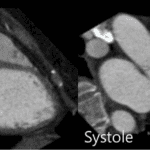
- Both stunned and hibernating myocardium represent dysfunctional but still viable myocardium
- a) Stunned myocardium
- “Myocardial stunning” occurs when myocardium exhibits persistent contractile dysfunction after an episode of ischemia, despite restoration of normal perfusion.
- Perfusion (O), Wall motion (X)
- A transient phenomenon that is followed by full functional recovery, usually after no more than several hours.
- b) Hibernating myocardium
- The result of chronically reduced resting perfusion, which can be reversed with restoration of adequate perfusion.
- Perfusion (X), Wall motion (X)
- a) Stunned myocardium
- Both stunned and hibernating myocardium represent dysfunctional but still viable myocardium
2. Myocardial infarction
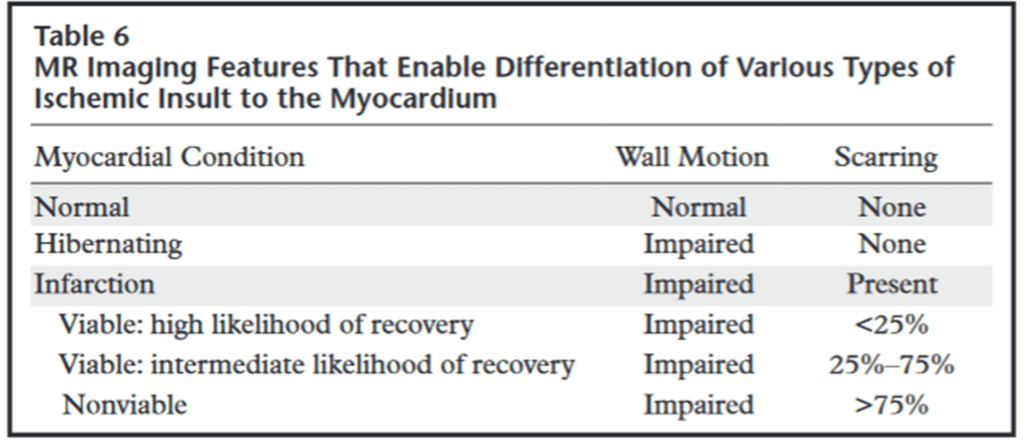
a) Delayed contrast enhancement on MRI
– 10 to 15 mins after administration of gadolinium ➜ Inversion recovery (T1 time x 0.69) ➜ signal nulling of normal myocardium
– Enhancing portion = Infarcted myocardium (bright is dead)
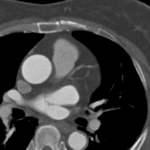
– Dark signal area inside of enhancing portion = No-reflow zone ; *microvascular obstruction (MVO) ➜ Poor prognosis
– Contrast material in acute intracellular area
b) T2WI
– high signal instensity area = edema or peri-infarct area
What is the mechanism of delayed enhancement in acute myocardial infarction?
Myocyte membrane rupture ➜ Passive diffusion of contrast material into the intracellular space ➜ increased tissue-level contrast agent concentration ➜ delayed hyperenhancement
2-1) Acute myocardial infarction
– Positive remodeling, no wall thinning
– Due to edema DCE area is exaggerated more than myocardial infarction area
– Native T1 value increased (edema)
– “No reflow” zone (microvascular obstruction
2-2) Chronic myocardial infarction
– Increased insterstitial space between collagen fibers in scar tissue
– Wall thinning due to fibrosis or scarring
– Fat deposit
– The margin becomes clearer as it progresses to chronicity, more accurately matching the area of myocardial infarction.
– Contrast material in insterstitial space
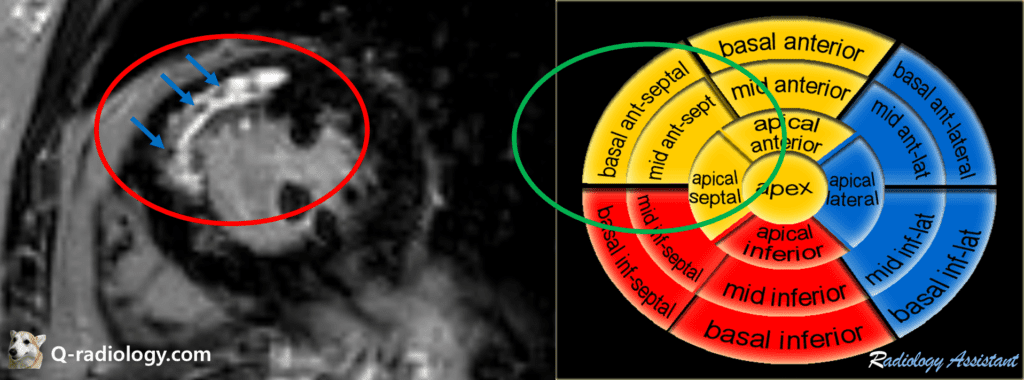
Note that dark signal area exists inside of enhancing portion indicates microvascular obstruction(MVO).
Image from radiologyassisstant
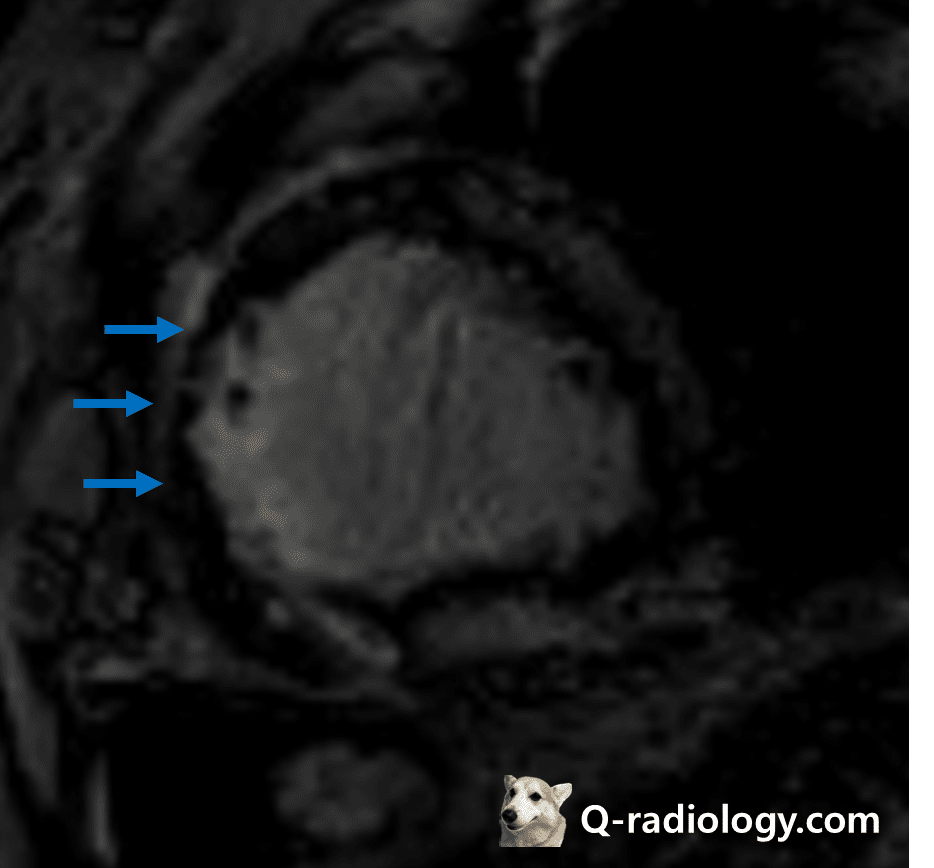
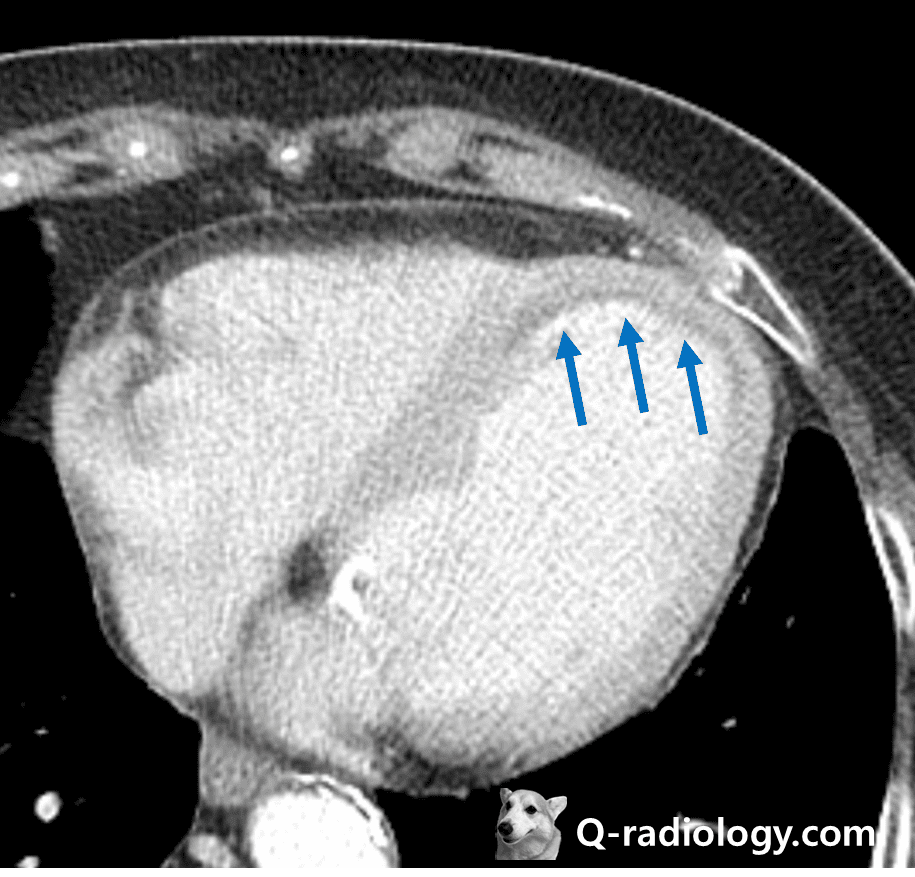
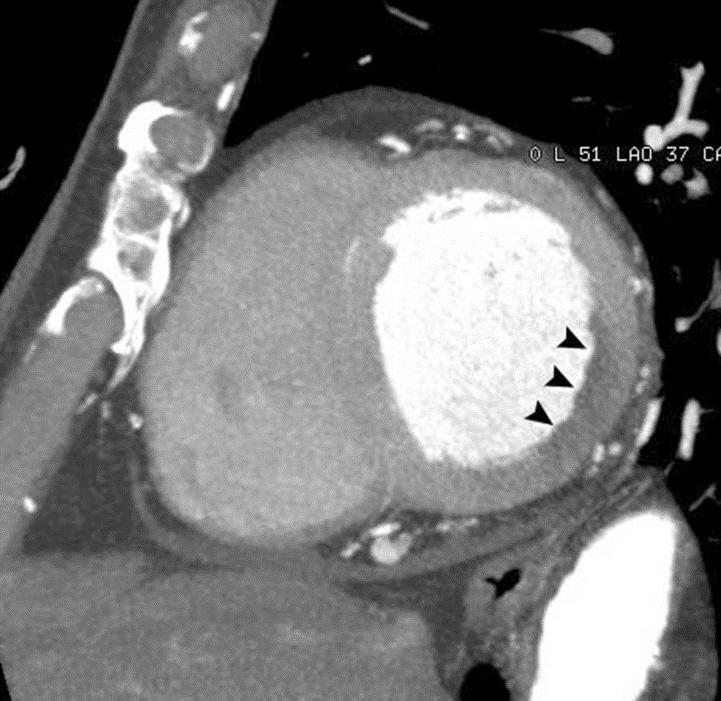
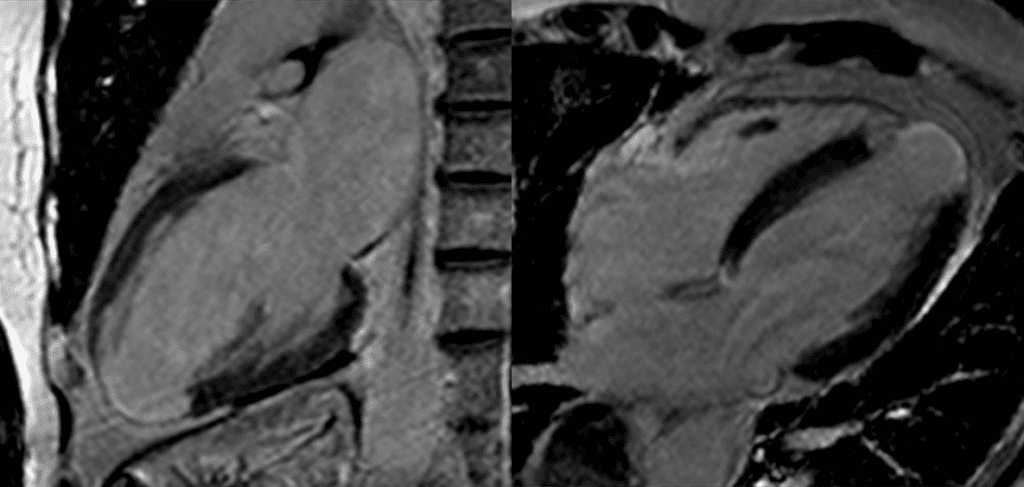
suggestive acute myocardial infarction.
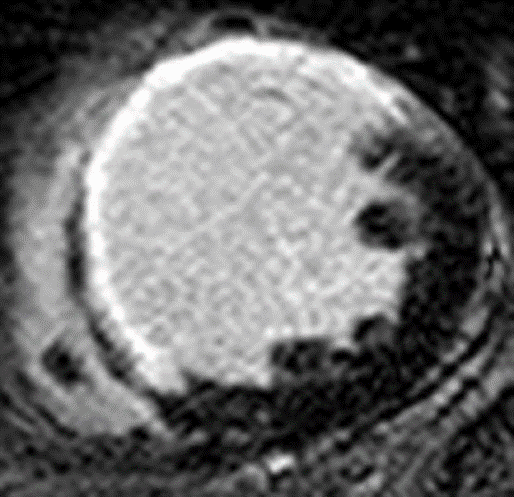
Transmural infarction.
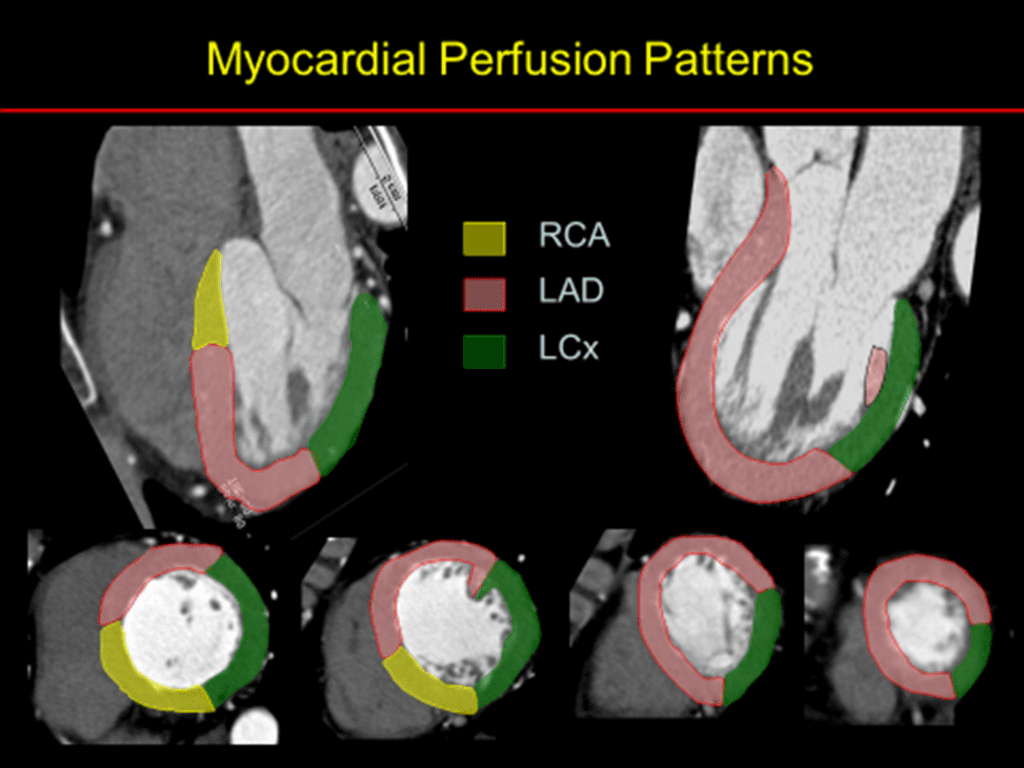
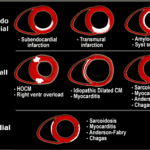
See more informations about cardiomyopathy in my website