DEFINITION OF Hemochromatosis
Iron overload disorder in which the involved organs store too much iron.
Hemochromatosis: Classified into 2 types
– Primary (hereditary): Autosomal recessive
– Secondary: Due to increased iron intake, transfusions,
etc
DEFINITION OF Hemosiderosis
– Increased iron deposition in involved organ without damage
IMAGING
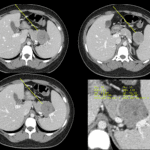
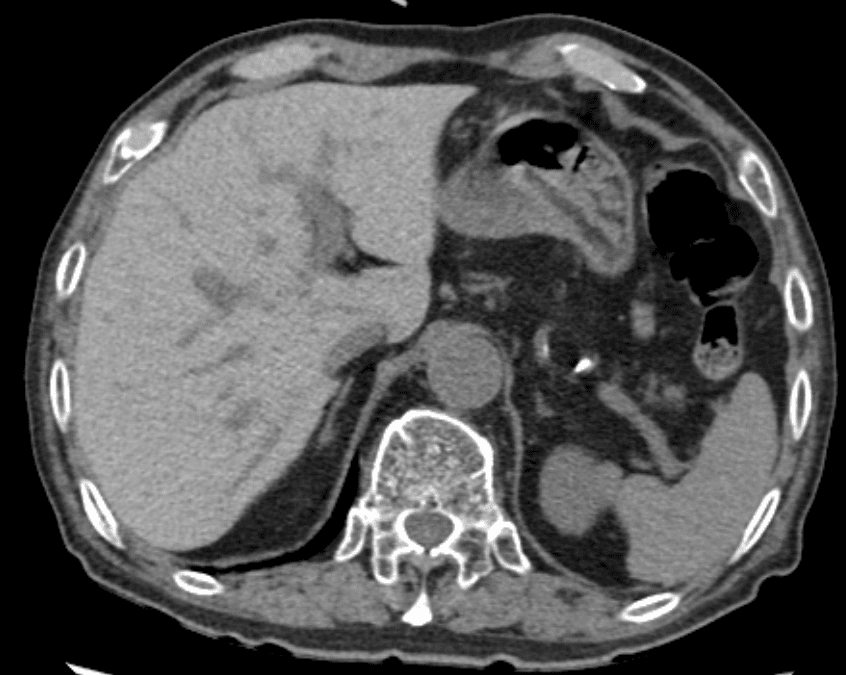
– Liver that is hyperdense on NECT and markedly hypointense on T2WI or in-phase GRE MR
– Primary (hereditary) hemochromatosis
; Affects parenchymal cells of liver, pancreas, and heart
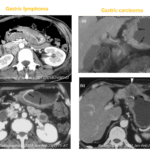
– Secondary hemochromatosis
; Affects RES: Liver, spleen, nodes
Presentation
• Most common signs/symptoms
– Asymptomatic during 1st decade of disease
– Classic triad of primary hemochromatosis : Cirrhosis, diabetes, hyperpigmented skin
– Other signs/symptoms
– Congestive heart failure, arrhythmias
– Arthralgias, impotence, gonadal atrophy
• Complications
– Periportal fibrosis leads to cirrhosis in late stage
– Hepatocellular carcinoma (14-30%)
– Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (30-60%)
– Cardiac failure (30%)
Demographics
• Gender
– M:F = 10:1
– Women protected by iron loss during menstruation and pregnancy
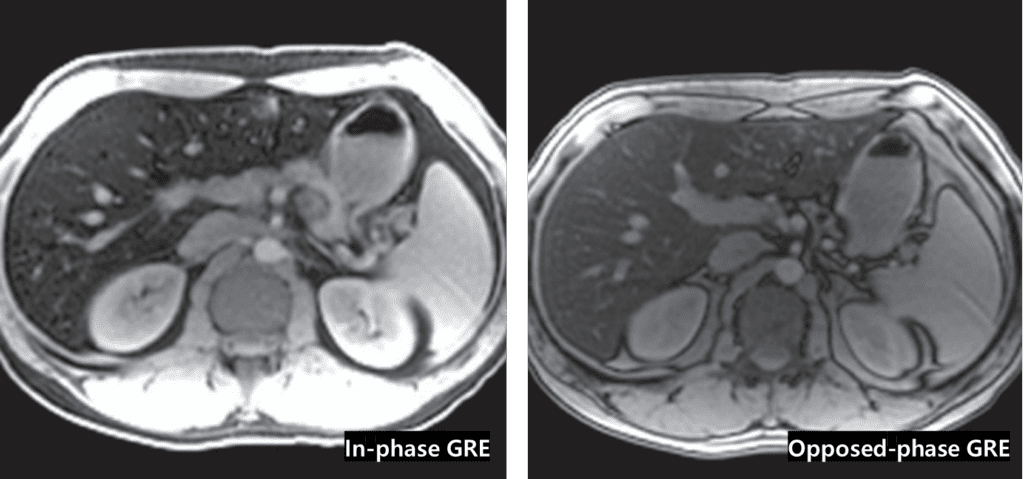
no signal loss on opposed-phse GRE, characteristic finding of excess hepatic iron