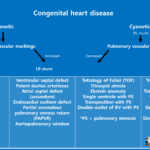
What is the coarctation of aorta
Coarctation of the aorta is a congenital vascular abnormality described as a narrowed or stenotic area within the aortic lumen most commonly distal to the left subclavian artery at the site of the aortic ductal attachment or ligamentum arteriosum.
It represents 6–8% of all congenital heart defects and is more commonly found in males than in females, with a 2:1 ratio.
Variant types can occur proximal to the left subclavian artery and rarely in the abdominal aorta.
Imaging finding of the coarctation of aorta
CT
– Direct visualization of coarctation and collaterals
X-ray
– A classic ‘3 sign’ on x-ray
Knob – Coarctation – Poststenotic dilation
– Notching & resorption of the lower part of the ribs
d/t collateral arteries
Collateral development along internal thoracic artery and intercostal artery due to pressure gradient.
Reference)
Charles S. White, Linda B. Haramati, Joseph Jen-Sho Chen, and Jeffrey M. Levsky (2014), Cardiac Imaging, Oxford university press